Wireless charging
Overview of the status and impact of the innovation
What
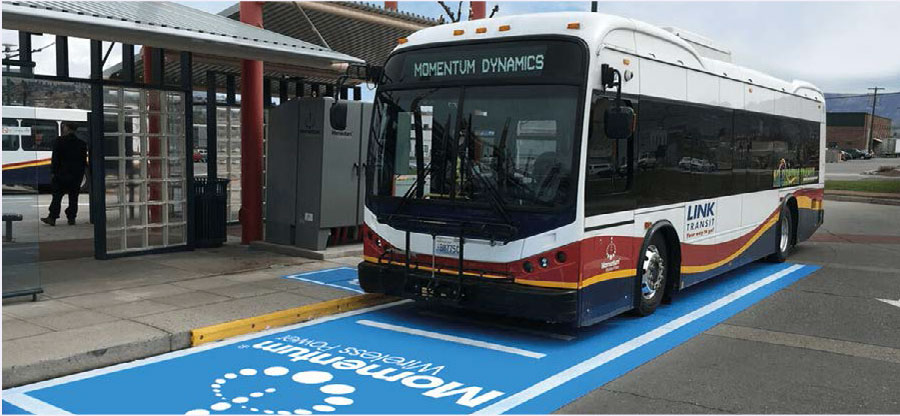
Wireless charging – now used for cell phones, watches and other small devices – is increasingly used for EVs, with efficiencies improving over time. EVs can be charged wirelessly via power transmitters in the ground when parked (static charging) or moving (dynamic charging).
Why
Wireless charging eliminates the need for the bulky cables and connectors at charging stations. It is equally suitable for large trucks that must travel long distances and for vehicles moving along busy roads in cities. It is also effective for fleets of buses or delivery vehicles (Box 3.5). However, wireless EV charging is capital intensive and requires more research and development.
BOX 3.5 Wireless charging solutions
The IPT-PRIMOVE system uses energy induction to charge light or heavy-duty vehicles, allowing them to charge automatically at pickup or waiting points. For example, IPT wireless charging infrastructure at one or both ends of a route allows buses to charge for 5-10 minutes while waiting, and it is being tested in London, Bristol, Madrid, Aachen and other cities (IPT Technology, 2021).

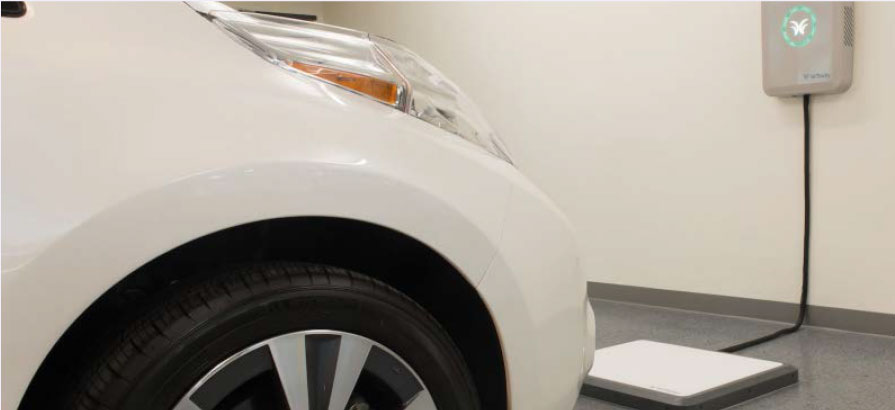
In China, Hongqi E-HS9, a Chinese car marque, is equipped with an 11-kW wireless charging system, which works together with an auto parking assist function to enable automatic parking and charging of the vehicles. Similarly, IM Motors' L7 provides a mass production solution of an 11-kW wireless charging system. The IM L7 can park automatically and start wireless charging.

Related kits
Power to mobility innovations
Innovations (35)
-
Technology and infrastructure
- 1 EV model evolution
- 2 EV batteries
- 3 Battery recycling technology
- 4 Diversity and ubiquity of charging points
- 5 Wireless charging
- 6 Overhead chargings
- 7 Portable charging stations
- 8 V2G systems
- 9 Digitalisation for energy management and smart charging
- 10 Blockchain-enabled transactions
- 11 Smart distribution transformers
- 12 Smart meters and submeters
-
Market design and regulation
-
System planning and operation
- 20 Cross-sectoral co-operation and Integrated planning
- 21 Including EV load in power system planning
- 22 Grid data transparency
- 23 Clean highway corridors
- 24 Operational flexibility in power systems to integrate EVs
- 25 Management of flexible EV load to integrate variable renewable energy
- 26 Management of flexible EV load to defer grid upgrades
- 27 EV as a resilience solution
-
Business models