Coupling cooling loads with solar generation
Overview of the status and impact of the innovation

What
Given the close match between the profiles of solar generation and cooling demand, energy planners can help meet cooling demand (especially as it increases) by deploying additional PV systems. In particular, energy planners can identify suitable rooftops or other surfaces for PV systems and ensure that the electricity grid is capable of integrating large numbers of distributed solar PV arrays.
Why
Effective deployment of solar energy would significantly decarbonise the cooling supply. It could also reduce dependence on the grid, increasing resilience and enabling people in remote locations with unreliable grid access to use cooling systems for critical purposes such as refrigerating food or medicines.
BOX 6.16 Coupling cooling loads and solar PV generation in Arizon
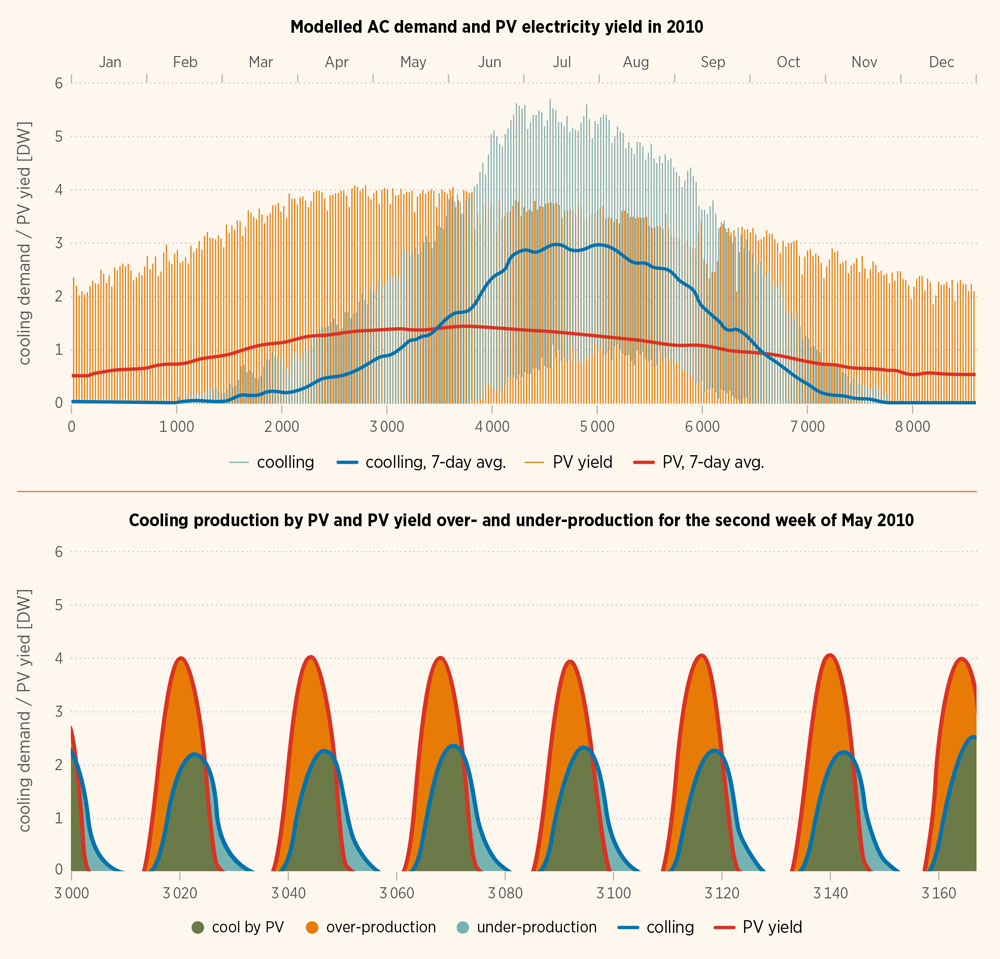
Figure 6.10 shows the correlation between seasonal and daily demands and PV electricity yield in an Arizona county. The Figure illustrates how solar generation can meet 55% of the cooling electricity demand on an hourly basis (Laine et al., 2019). Even more of the demand could be met if buildings were pre-cooled during the sunniest hours, taking advantage of the buildings’ thermal storage capabilities.
FIGURE 6.10 AC demand and PV electricity yield in Maricopa County, Arizona, 2010
Related kits
Power to heat and cooling innovations
Innovations (35)
-
Technology and infrastructure
- 1 Low-temperature heat pumps
- 2 Hybrid heat pumps
- 3 High-temperature heat pumps
- 4 Waste heat-to-power technologies
- 5 High-temperature electricity-based applications for industry
- 6 Low-temperature thermal energy storage
- 7 Medium- and high-temperature thermal energy storage
- 8 Fourth-generation DHC systems
- 9 Fifth-generation DHC systems
- 10 Internet of Things for smart electrification
- 11 Artificial intelligence for forecasting heating and cooling demands
- 12 Blockchain for enabling transactions
- 13 Digitalisation as a flexibility enabler
-
Market design and regulation
- 14 Dynamic tariffs
- 15 Flexible power purchase agreement
- 16 Flexible power purchase agreement
- 17 Standards and certification for improved predictability of heat pump operation
- 18 Energy efficiency programmes for buildings and industry
- 19 Building codes for power-to-heat solutions
- 20 Streamlining permitting procedures for thermal infrastructure
-
System planning and operation
-
Business models
- 28 Aggregators
- 29 Distributed energy resources for heating and cooling demands
- 30 Heating and cooling as a service
- 31 Waste heat recovery from data centres
- 32 Eco-industrial parks and waste heat recovery from industrial processes
- 33 Circular energy flows in cities – booster heat pumps
- 34 Community-owned district heating and cooling
- 35 Community-owned power-to-heat assets